HOW SUSTAIN ARE WE ? INDONESIAN DATA
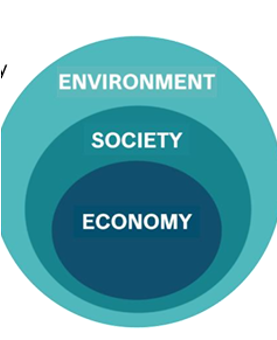
Sustainability encompasses a holistic approach aimed at preserving our planet for present and future generations. Originating from the influential Brundland Report of 1987, sustainable development seeks to balance environmental preservation with economic progress, ensuring the fulfilment of current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own. This comprehensive perspective explores into various dimensions of sustainability, including environmental, social, and economic aspects, highlighting their interdependence in fostering sustainable development.
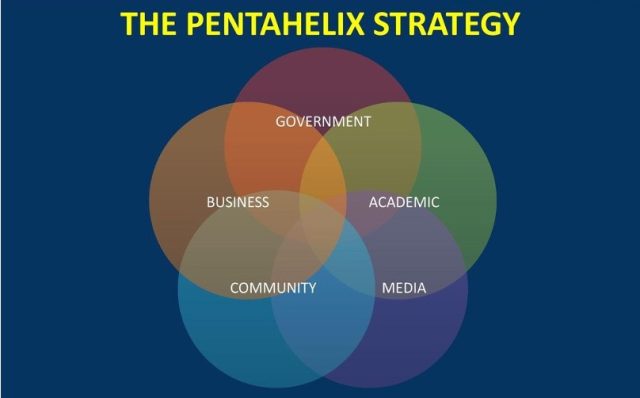
The Pentahelix strategy, elaborated upon, presents a collaborative framework involving academia, business, government, media, and the community. This approach, building upon the triple helix model, underscores the importance of partnerships among diverse stakeholders to foster innovation and ensure sustainable long-term growth. Moreover, on the global consensus embodied in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), comprising 17 interconnected objectives aimed at promoting environmental stewardship, prosperity, and equity by 2030. The necessity of measuring progress towards these goals is highlighted, with reference to the Sustainable Development Report as a crucial tool for assessing nations’ advancement.
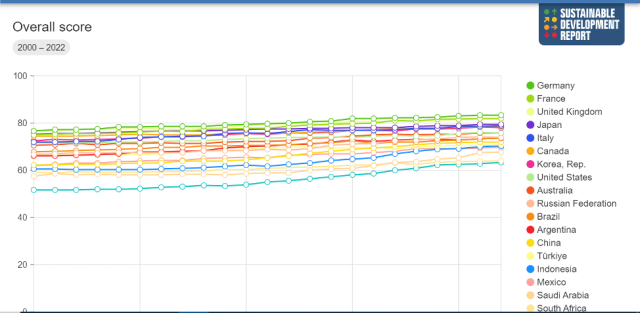
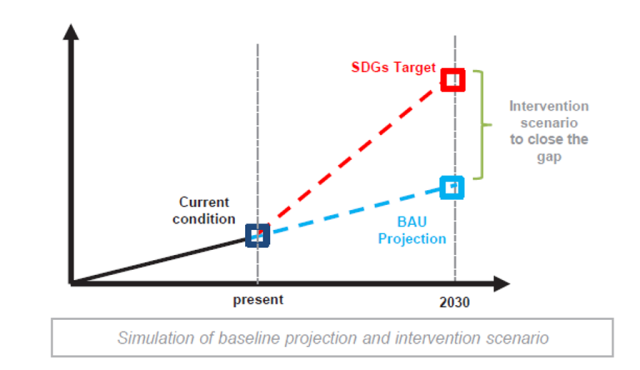
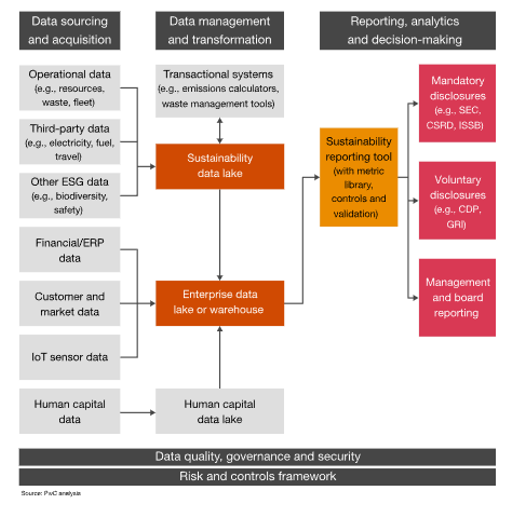
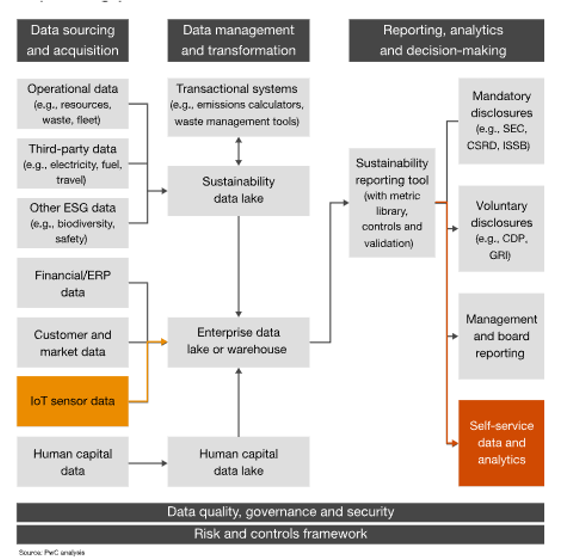
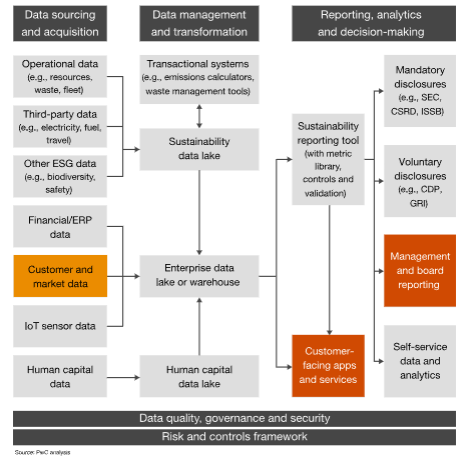
In Indonesia, specific Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) objectives are outlined, covering a diverse array of critical areas. These objectives encompass eradicating poverty, ensuring zero hunger, promoting good health and well-being, providing quality education, achieving gender equality, ensuring access to clean water and sanitation, promoting affordable and clean energy, fostering decent work and economic growth, facilitating industry, innovation, and infrastructure, reducing inequalities, building sustainable communities, taking climate action, preserving life on land, and fostering partnerships for the goals. Analysis of the SDG Dashboard highlights disparities between the current development levels in Indonesia and the targeted objectives set by the SDGs. This analysis underscores the urgent need for intervention to address existing inequities and accelerate progress towards achieving these objectives. Additionally, the concept of greenwashing, or the deceptive practice of presenting an environmentally friendly image while engaging in environmentally harmful activities, is examined through educational videos. This examination emphasizes the importance of transparency and authenticity in sustainability efforts, urging organizations to uphold genuine environmental commitments. Furthermore, comprehensive sustainability data is deemed essential for informed decision-making and value production. This necessitates the enhancement of reporting systems and the integration of data from various sources to provide a comprehensive understanding of sustainability issues. By leveraging robust sustainability data, policymakers, businesses, and communities can make informed decisions and implement effective strategies to advance sustainable development goals in Indonesia and beyond.

Moreover, insights from a study on the relationship between Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) indices and investment decisions are shared. Through surveys and interviews, factors influencing investors’ preferences are elucidated, offering valuable guidance for stakeholders seeking to leverage ESG principles to attract investment. Furthermore, the transformative potential of technology in advancing sustainable goals is highlighted, with emphasis on innovative solutions such as renewable energy and sustainable agriculture to address environmental challenges effectively.
Ultimately, the insights presented serve as a rallying cry for collective action towards achieving global sustainability objectives. By harnessing comprehensive data, innovative technologies, and collaborative initiatives, a fundamental shift towards a more environmentally conscious and resilient future is advocated. These insights provide a roadmap for endeavors aimed at creating a sustainable and prosperous future in our interconnected world.

